Walk into any electronics store and the options can feel endless. Rows of machines with similar shapes, flashy names, and confusing specs—it’s enough to make anyone hesitate. Yet behind those lookalike devices are very different types of printers built for specific needs. Some are designed for speed, others for quality, and a few are made for very particular jobs you might not expect from a printer at all.
So why does this matter? Because buying the wrong printers type can mean wasted money, frustration, and even downtime when you need it most. Picture this: a student rushing to print an assignment minutes before class, only to find the printer spits out streaky pages because it wasn’t designed for heavy color printing. Or a small business owner burning through expensive ink cartridges when a different types of printers could have cut costs in half.
This guide breaks everything down. We’ll explore every major printers type in detail—how they work, what they do best, and when to use them. From inkjet to laser, from photo printers to thermal devices, you’ll learn not only what exists but also how to choose wisely. We’ll even include comparison tables designed for quick reference so you can make decisions confidently. By the end, you’ll know exactly which types of printers fit your home, office, or creative projects.
Before diving into the details, let’s talk about why understanding printer types isn’t just useful—it’s essential.
Why Understanding Printer Types Matters
Printers are easy to take for granted until they stop working or fail to meet expectations. Many people assume one machine can handle everything, but the reality is very different. Each printers type has strengths and weaknesses that affect cost, speed, quality, and even reliability.
For example, some types of printers shine when printing photos but choke on large text documents. Others breeze through hundreds of pages per day but produce average image quality. Without knowing these differences, you might overspend on features you don’t need—or worse, end up with a printer that can’t keep up.
For businesses, this isn’t just an inconvenience. A mismatch between printing needs and printer capability can mean real financial loss. Time spent fixing jams or waiting on slow prints adds up. That’s why learning about every major printers type helps prevent headaches later.
Main Types of Printers and Their Uses
Now that we understand why knowing the types of printers matters, let’s move into the core of this guide: breaking down every major printers type you’ll encounter. This is where things get practical. We’ll look at how each type printer works, its strengths and limitations, and where it fits best.
By comparing these types of printers, you’ll see that choosing the right one isn’t about getting the most expensive model but finding the perfect match for your real-world needs.
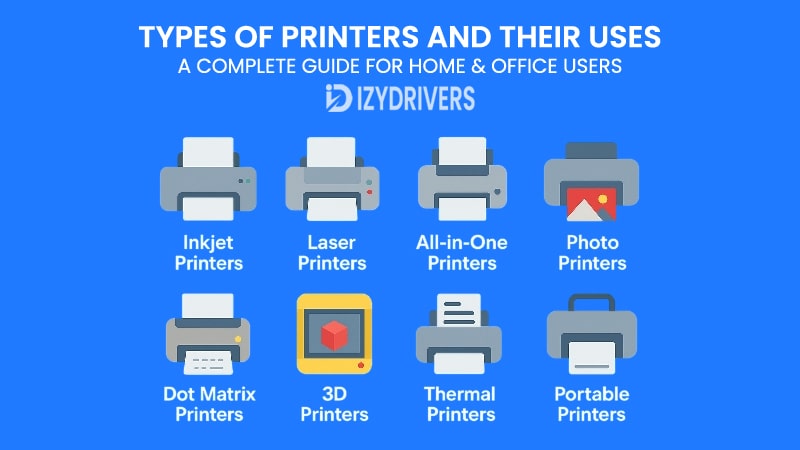
Inkjet Printers
Inkjet printers are perhaps the most common printers type for households and students. They work by spraying tiny droplets of liquid ink directly onto paper, allowing for high-resolution prints with vibrant colors. This makes them ideal for school assignments, family photos, and general home use. They handle both text and images fairly well, so if you need flexibility, inkjets are a good choice.
However, this printers type comes with trade-offs. Ink cartridges can be pricey, and frequent printing might make the cost-per-page higher than you’d like. Additionally, they tend to be slower compared to laser printers, so if speed is essential, inkjets might leave you waiting longer than you want. Still, for users prioritizing quality over volume, inkjet printers often strike the right balance.
Laser Printers

Switching gears to speed and efficiency, laser printers dominate offices and workplaces where high-volume printing is routine. Instead of liquid ink, they use toner powder fused to paper with heat, allowing them to churn out pages much faster than inkjets. For text-heavy documents, this printers type delivers sharp, clear results quickly and consistently.
Another advantage is cost efficiency. While the initial price tag might be higher, the toner lasts longer, and the cost per page is significantly lower over time. That makes this printers type a smart investment for businesses or anyone printing large volumes regularly. The only real downside? Color laser printers can be expensive, and they typically take up more space than compact inkjets.
All-in-One Printers

All-in-one printers, sometimes called multifunction printers, combine printing, scanning, copying, and sometimes even faxing into a single device. This printers type is popular with home offices and small businesses because it saves space and often costs less than buying separate machines for each task.
The convenience factor is undeniable. Need to scan a signed document and print it right away? No problem. However, while all-in-ones cover multiple functions, they may not excel in any single area. Print quality and speed might be average compared to dedicated types of printers designed solely for one purpose. Still, for everyday tasks, they offer excellent value.
Photo Printers
As the name suggests, photo printers focus on producing high-quality images. This printers type uses specialized ink and paper to deliver professional-grade prints that capture fine details and accurate colors. Photographers, designers, and creative professionals often rely on these printers to bring digital art to life.
The trade-off is versatility. Photo printers usually handle standard document printing poorly or not at all. They’re built for one thing—printing stunning photos—and they do it exceptionally well. If you rarely print images, other types of printers will likely suit your needs better.
Dot Matrix Printers
While they might seem like relics from the past, dot matrix printers still hold a place in specific industries. This printers type uses impact printing, striking an ink-soaked ribbon against paper to create characters. The result isn’t pretty—resolution is low—but the durability and ability to print through carbon copies make them valuable for tasks like invoices and shipping forms.
Another advantage is cost. Dot matrix printers are cheap to operate and withstand harsh environments like warehouses. So while most modern offices have moved on, this printers type survives where reliability beats aesthetics.
3D Printers

One of the most exciting modern developments, 3D printers go beyond paper entirely. They build physical objects layer by layer using materials like plastic or resin. This printers type has revolutionized fields like prototyping, medical implants, and even education, where students can design and print real-world models.
The downside? Complexity and cost. Learning to use 3D printers effectively takes time, and materials can be expensive. Still, as technology advances, this printers type becomes more accessible, opening doors for innovation at home and in small businesses.
Thermal Printers

Finally, thermal printers specialize in printing receipts, labels, and shipping tags. Instead of ink or toner, this printers type uses heat-sensitive paper, making it incredibly fast and low-maintenance. Retail stores, logistics companies, and restaurants often rely on thermal printers because they’re cheap to run and rarely jam.
The limitation is clear: thermal printers aren’t for documents or images. They exist for specific, practical tasks and do them well. If you don’t need receipts or labels, other types of printers will serve you better.
Portable Printers

Portable printers have gained popularity among professionals and travelers who need printing capabilities on the go. This printers type is compact, lightweight, and often battery-powered, making it possible to print documents or photos anywhere without relying on a traditional office setup.
The biggest advantage of portable printers is convenience. They connect easily to smartphones or laptops via Bluetooth or Wi-Fi, allowing quick prints during client meetings, business trips, or even in cars. However, their small size means limited paper capacity, slower speeds, and higher costs per page compared to standard types of printers. Still, for those who value mobility over volume, portable printers are an excellent solution.
Comparison Table of Types of Printers and Their Uses
| Printer Type | Ideal Use Case | Advantages | Disadvantages | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inkjet Printers | Home use, photo printing | High-quality prints, affordable upfront cost | Slower speed, expensive ink | Students, families, low-volume printing |
| Laser Printers | Offices, high-volume printing | Fast, low cost per page, reliable | Higher initial price, larger size | Businesses, schools, heavy text printing |
| All-in-One Printers | Home offices, small businesses | Print, scan, copy, fax in one machine | Average in speed and quality | Remote workers, small offices |
| Photo Printers | Photography, creative professionals | Professional-grade image quality | Limited to photos, higher cost per page | Designers, photographers, artists |
| Dot Matrix Printers | Industrial use, multi-copy forms | Durable, low-cost operation | Noisy, low-resolution output | Warehouses, logistics, industrial setups |
| 3D Printers | Prototyping, education, manufacturing | Prints 3D objects, innovative applications | Expensive, steep learning curve | Engineers, educators, product designers |
| Thermal Printers | Receipts, labels, shipping tags | Fast, no ink needed, low maintenance | Limited to receipts/labels only | Retail, restaurants, shipping companies |
| Portable Printers | Mobile professionals, travelers | Lightweight, wireless, prints on the go | Limited speed, smaller capacity, costlier | Business travelers, field workers |
Printer Categories by Use Case
Now that we’ve explored all major types of printers in detail, it’s time to group them based on real-world usage scenarios. This approach helps readers quickly identify which printers type fits their specific needs rather than focusing solely on technical specs.
Home Printing Needs
For most households, printing is occasional rather than constant. Homework assignments, boarding passes, personal photos—these are the typical tasks. In this case, an affordable, compact printers type like an inkjet or all-in-one printer usually works best. They balance quality with price, offering decent performance without overkill features.
Portable printers are also gaining popularity for home use, especially among families who want to print photos or documents directly from smartphones. While not ideal for heavy workloads, this Home Printers delivers convenience for light, everyday printing.
Office & Business Printing
Businesses demand reliability, speed, and low cost per page. That’s why laser printers dominate this category. For high-volume document printing, this printers type provides fast output, durable performance, and professional-quality text.
All-in-one printers also shine here because they combine multiple functions—printing, scanning, copying—into one device. For small businesses or startups, this saves both space and money while maintaining productivity.
Creative & Professional Printing
Graphic designers, photographers, and artists have different priorities: color accuracy, resolution, and print quality. Profesional Photo printers and some high-end inkjets meet these demands by producing gallery-worthy prints. For 3D modeling professionals, 3D printers belong in this printers type category because they bring digital designs into the physical world.
This group often requires specialized printer paper, advanced color profiles, and sometimes wireless capabilities for faster workflows. Investing in the right types of printers here can significantly improve output quality.
Industrial & Specialized Printing
Finally, some environments need rugged, purpose-built machines. Dot matrix printers continue to serve in warehouses where multi-part forms are standard. Thermal printers handle receipts, shipping labels, and barcodes quickly and affordably.
For fieldwork or logistics operations, portable printers also fit this printers type category because mobility matters. Whether printing invoices on-site or labels in remote locations, these machines deliver practical solutions where standard printers fall short.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a Printer
Choosing the right printer isn’t just about knowing the types of printers available. It’s also about understanding how each feature impacts your daily use. A well-informed decision prevents costly mistakes and ensures your printer matches your real needs.
Below are the most important factors to consider before buying any printers type:
Printing Speed & Volume
If you print frequently or handle large documents, speed matters. Laser printers typically offer faster output, while inkjets prioritize quality over speed. Consider how many pages per minute (PPM) you need. High-volume offices benefit from printers with higher duty cycles, meaning they can handle thousands of pages each month without issues.
On the other hand, for occasional home printing, a slower printers type might be acceptable if it delivers better quality or lower upfront costs.
Print Quality & Resolution
Resolution is measured in dots per inch (DPI). The higher the DPI, the sharper the output. Photo printers and high-end inkjets offer superior resolution for images and graphics, while standard office printers focus on clear text. Ask yourself whether you need professional-grade prints or just basic documents before choosing a printers type.
Connectivity & Compatibility
Modern printers come with various connection options: USB, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and even cloud printing services. For offices, network-ready types of printers allow multiple users to print wirelessly, increasing convenience and productivity. Compatibility with smartphones, tablets, and laptops also adds flexibility.
Cost Per Page & Maintenance
Initial price tags can be misleading. Some printers are cheap upfront but expensive to maintain because of costly ink or toner. Check the cost per page (CPP) to understand long-term expenses. A slightly pricier printers type might save money over time if it uses affordable consumables.
Eco-Friendly & Energy-Efficient Options
Sustainability matters more than ever. Many modern printers come with energy-saving modes, duplex printing (double-sided), and eco-friendly ink options. If environmental impact is a concern, look for types of printers with Energy Star ratings or similar certifications.
Common Mistakes When Choosing a Printer
Even with all the information about different types of printers, many people still end up with the wrong device. Why? Because certain assumptions and oversights lead to poor choices. Let’s go through the most common mistakes so you can avoid them when selecting any printers type.
Focusing Only on Upfront Cost
It’s tempting to buy the cheapest printer available, especially when budgets are tight. However, the initial price doesn’t reflect long-term expenses. Some types of printers come with low sticker prices but require expensive ink or toner refills. Over time, you might spend far more than you expected on maintenance.
A better approach is to consider the total cost of ownership, including consumables, paper, and energy usage. This helps you find a printers type that balances affordability with sustainability.
Ignoring Print Volume Needs
Another mistake is underestimating how much you print. A compact inkjet might be fine for occasional use, but it will struggle in a busy office environment. Printers have monthly duty cycle ratings—ignore them, and you risk constant breakdowns, paper jams, or costly repairs.
When in doubt, choose a printers type rated slightly above your expected usage. It’s better to have extra capacity than to overwork a smaller machine.
Overlooking Connectivity Options
Modern workplaces and homes rely heavily on wireless devices. Yet many buyers forget to check whether a printer supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or mobile printing. Without these features, sharing the printer across multiple devices becomes frustrating.
Make sure the types of printers you’re considering offer the right connectivity for your setup—especially if you work remotely or collaborate with others.
Forgetting About Space and Noise
Some printers, especially high-end laser models or dot matrix units, take up considerable space and can be noisy. Buying one without measuring your available area or considering noise levels might disrupt your workspace.
Portable and all-in-one printers type models often solve these problems by offering compact, quieter designs without sacrificing too much functionality.
Neglecting Driver and Software Support
A powerful printer is useless if it doesn’t play well with your computer or operating system. Always check printer driver availability, software compatibility, and update frequency before committing to any printers type. This ensures smooth performance across devices and platforms.
How to Maintain Your Printer for Longer Life
Buying the right types of printers is only half the battle. Proper maintenance ensures that your printer lasts longer, performs better, and avoids unnecessary repairs. Many people overlook this step, but with a few simple habits, you can significantly extend the lifespan of any printers type.
Regular Cleaning and Dust Removal
Printers attract dust, paper fibers, and ink residue over time. This buildup can affect print quality and even cause jams. Wipe the exterior regularly and, if the manual allows, clean the internal printer rollers gently. Some types of printers even come with built-in cleaning cycles for print heads—use them as recommended.
A clean printer not only works better but also prevents costly repairs in the long run.
Using Quality Paper and Ink
Low-quality paper may seem cheaper, but it often sheds more fibers, leading to clogs and roller wear. Similarly, generic or counterfeit ink cartridges might save money upfront but can damage print heads or void warranties. Always use paper and ink recommended by the printers type manufacturer for optimal performance.
Updating Firmware and Drivers
Printer manufacturers release updates to fix bugs, improve compatibility, and add features. Skipping these updates might cause printing errors or connectivity issues. Check the official website for the latest drivers and firmware for your types of printers model.
Managing Power and Storage Conditions
Unplugging printers during long periods of inactivity prevents power surges from damaging internal circuits. Also, avoid exposing your printers type to extreme heat, humidity, or direct sunlight, as these conditions can degrade components over time.
Scheduling Preventive Maintenance
For offices with heavy printing needs, scheduling professional maintenance every few months keeps printers running smoothly. Technicians can replace worn-out printer parts before they fail completely, reducing downtime and repair costs.
Conclusion
Choosing the right printer isn’t just about knowing the types of printers available—it’s about understanding your unique needs, budget, and long-term usage. From high-speed laser models for offices to compact portable printers for on-the-go tasks, there’s a printers type for every scenario. By learning about their features, common mistakes to avoid, and proper maintenance practices, you can save money, improve productivity, and extend your printer’s lifespan.
With the comparison table above, readers can now quickly identify the right types of printers for their specific requirements—whether at home, in the office, or for professional creative work.
FAQs About Types of Printers
What is the most cost-effective type of printer for home use?
Inkjet printers are often the best balance between quality and price for home users. However, if you print frequently, a laser printers type might save money on ink over time.
Which printer type is best for high-quality photo printing?
Photo printers or high-end inkjet printers deliver the best color accuracy and resolution for photography and creative projects.
Are portable printers worth it?
Yes, if you need printing on the go—such as for business trips or fieldwork—portable printers offer convenience and wireless connectivity in a compact design.
How often should I maintain my printer?
Basic cleaning every few weeks and professional servicing every 6–12 months (for heavy use) helps extend the life of any printers type.
What factors matter most when choosing a printer?
Key considerations include print speed, quality, cost per page, connectivity options, and long-term maintenance costs.