When you hit the print button on your computer, you expect your document to appear on paper exactly as it looks on the screen. But behind that simple click, a lot of processes happen — and one key component that makes it possible is the PCL Driver.
Short for Printer Command Language, PCL Drivers act as the bridge between your computer and the printer. Without the right driver, even the most advanced printer can’t interpret your computer’s instructions correctly, leading to printing errors, formatting issues, or no output at all.
Over the years, PCL has become one of the most widely used printing languages in the world because of its speed, reliability, and compatibility across different printer models and operating systems. Whether you’re setting up a printer for home use, managing a busy office, or troubleshooting printing errors, understanding PCL Drivers will help you get better performance and fewer headaches.
This guide takes you through everything you need to know about PCL Drivers — from what they are, how they work, and the different versions available, to installation steps, troubleshooting tips, and best practices. By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how to keep your printing environment running smoothly.
What is a PCL Driver?
A PCL Driver, short for Printer Command Language Driver, is specialized software that allows your computer and printer to communicate effectively. When you send a document to print, the data doesn’t go directly to the printer in its original format. Instead, the PCL Driver converts the file into a language the printer can understand, ensuring that text, images, and layouts appear exactly as intended.
Originally developed by Hewlett-Packard (HP) in the 1980s, PCL quickly became one of the most widely used printer languages in the world. Its success came from three main strengths:
- Speed: PCL processes print jobs faster than many competing languages.
- Compatibility: It works with a wide range of printers and operating systems.
- Efficiency: PCL uses less memory, which makes it ideal for office environments with high printing volumes.
Over time, different versions of PCL have been released. For example, PCL5 was known for its simplicity and broad compatibility, while PCL6 introduced enhanced graphics, better color support, and improved print quality. Many manufacturers also provide Universal PCL Drivers, allowing a single driver to work across multiple printer models, reducing the complexity of driver management.
It’s important to note that PCL is different from other print languages like PostScript or GDI. PostScript, for instance, is often preferred for graphic design due to its superior image handling, while GDI relies heavily on the Windows operating system for rendering. PCL strikes a balance by offering speed and quality, making it ideal for both text documents and everyday graphics.
Simply put, without a PCL Driver, your computer and printer would be speaking entirely different languages — and your print jobs wouldn’t turn out as expected.
How PCL Drivers Work
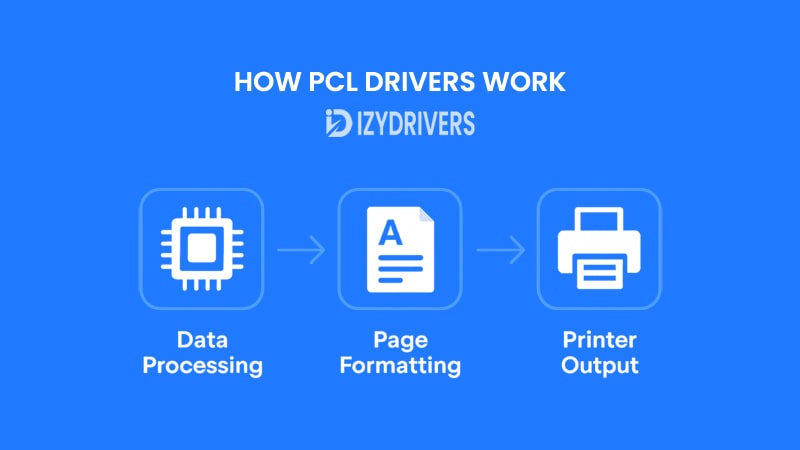
While most users simply click “Print” and expect perfect results, the process behind the scenes is far more sophisticated. A PCL Driver acts like a translator, turning your digital file into printer-friendly commands. This ensures that text, graphics, fonts, and layouts are reproduced accurately on paper. The workflow can be divided into three key stages: Data Processing, Page Formatting, and Printer Output.
Data Processing
When you start a print job, the PCL Driver first receives the raw data from your computer. This includes text, images, fonts, and formatting instructions from the document. Instead of sending this information directly to the printer, the driver converts it into PCL commands — a standardized set of instructions understood by printers that support the PCL language.
At this stage, the driver also optimizes the data to reduce file size without sacrificing quality, allowing faster transmission to the printer. This efficiency is one reason why PCL has become popular in offices handling large print volumes.
Page Formatting
After the data is processed, the next step is page formatting. The PCL Driver decides how each page will look, handling tasks such as:
- Text alignment and margins
- Image placement and scaling
- Font substitution if the printer lacks specific fonts
For color printers, this stage also involves translating RGB or CMYK color data into commands that the printer can render accurately. PCL6, for example, provides enhanced color handling compared to earlier versions like PCL5.
Printer Output
Finally, the formatted PCL commands are sent to the printer, which interprets them and produces the physical page. Because the printer already has all the instructions before printing begins, the process is efficient and consistent, reducing errors like misaligned text or missing graphics.
This three-step workflow makes PCL Drivers ideal for both simple text documents and moderately complex graphics, offering a good balance between speed, quality, and compatibility.
Types of PCL Drivers

Over the years, several versions of PCL Drivers have been released, each designed to meet evolving printing needs. Knowing the differences helps you choose the right one for your printer and workflow. The three most common categories are PCL5, PCL6, and Universal PCL Drivers.
PCL5 Drivers
Introduced in the early 1990s, PCL5 quickly became a standard for office printing. It supports both text and simple graphics, offering wide compatibility across many printers and operating systems. PCL5 drivers are lightweight, easy to set up, and work well with legacy printers still in use today.
However, PCL5 has limitations when handling complex graphics or high-resolution images. It was primarily designed for speed and basic document printing rather than professional-grade photo or color work.
Best for: Offices with older printers, simple text documents, and basic graphics.
PCL6 Drivers
Launched later, PCL6 brought significant improvements over PCL5. It features a modular architecture for better performance, enhanced error handling, and superior graphics rendering. PCL6 also supports higher print resolutions, producing sharper text and more vibrant images compared to PCL5.
Another advantage of PCL6 is its compression technology, which reduces the size of print jobs. This allows faster data transfer between computer and printer, making it suitable for busy office environments with heavy printing demands.
Best for: Modern printers, high-resolution prints, and environments requiring speed and quality.
Universal PCL Drivers
Many manufacturers now offer Universal Print Drivers (UPD) that support multiple printer models using a single driver package. This simplifies IT management because you no longer need separate drivers for every printer in the office.
Universal PCL Drivers often include both PCL5 and PCL6 modes, giving you flexibility based on your printing needs.
Best for: Large offices, mixed printer environments, and IT departments managing multiple devices.
PCL5 vs PCL6 vs Universal PCL Drivers: Key Differences Explained
| PCL Driver Type | Key Features | Advantages | Limitations | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL5 Driver | Basic text & graphics support | Wide compatibility, lightweight, stable | Limited resolution, basic graphics handling | Older printers, simple office documents |
| PCL6 Driver | Enhanced graphics & modular design | High resolution, faster processing, better color handling | Requires newer printers, slightly complex setup | Modern printers, high-quality & heavy printing |
| Universal PCL Driver (UPD) | Single driver for multiple printers | Simplifies IT management, supports PCL5 & PCL6 modes | May not unlock all printer-specific features | Large offices, mixed printer environments |
Key Functions and Features of PCL Drivers

The PCL Driver is more than just a link between your computer and printer — it comes with specific functions designed to enhance printing speed, accuracy, and compatibility. Understanding these features helps you choose the right driver for your needs and maintain consistent print quality.
Speed and Performance
One of the biggest advantages of PCL Drivers, especially PCL6, is their ability to handle print jobs quickly. By processing most page formatting tasks on the computer rather than the printer itself, PCL Drivers reduce the printer’s workload. This leads to:
- Faster data transfer from PC to printer
- Quicker job processing for text-heavy documents
- Reduced printing bottlenecks in busy office environments
For offices that print hundreds of pages daily, this speed advantage makes a noticeable difference in productivity.
Quality and Resolution
While PCL5 offers good print quality for basic needs, PCL6 significantly improves resolution and color accuracy. PCL6 supports advanced imaging features such as:
- Higher DPI (dots per inch): Produces sharper text and detailed images
- Improved color gradients: Smoother transitions in photos and graphics
- Better vector graphics support: Ideal for charts, diagrams, and mixed documents
This makes PCL6 suitable for professional reports, presentations, and even moderate photo printing.
Printer Compatibility
PCL Drivers are known for their broad compatibility across printer models and operating systems. Whether you’re using a legacy HP LaserJet or a modern multifunction printer, there’s likely a PCL driver available for it.
Universal PCL Drivers go even further by offering:
- Single installation for multiple printer models
- Cross-platform support for Windows, macOS, and some Linux systems
- Simplified driver management for IT administrators
This compatibility ensures consistent results without needing separate drivers for each device.
Error Handling and Feedback
Modern PCL Drivers also provide real-time status feedback. If there’s a paper jam, low toner level, or connectivity issue, the driver can relay this information to the user. This minimizes downtime and helps troubleshoot problems faster.
Installing and Updating PCL Drivers
Getting your printer to work properly begins with installing the correct PCL Driver for your system. Without the right driver, the printer won’t receive the instructions it needs to produce accurate and high-quality prints. Below is a complete guide for installing and updating PCL Drivers on different platforms.
Downloading the Right PCL Driver
Before installation, visit the printer manufacturer’s official website — such as HP, Canon, or Ricoh — and search for drivers by printer model. Make sure to:
- Download the correct PCL version (PCL5, PCL6, or Universal).
- Match the driver with your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux).
- Check for 64-bit or 32-bit compatibility.
Using third-party websites is not recommended as they may provide outdated or unsafe files.
Installation Steps for Windows
- Download the correct PCL Driver from the manufacturer’s website.
- Extract the file if it comes in a compressed folder.
- Open Devices and Printers in the Windows Control Panel.
- Click Add a Printer → Add a Local Printer → Have Disk.
- Browse to the folder where the driver was downloaded and select the INF file.
- Follow the on-screen instructions to complete the installation.
After installation, set the new driver as the default printer driver to start using it immediately.
Installation Steps for macOS and Linux
- macOS:
- Download the driver package compatible with macOS.
- Open the file and follow the installation prompts.
- Add the printer via System Preferences → Printers & Scanners.
- Linux:
- Use the manufacturer’s Linux driver package or open-source alternatives like CUPS.
- Add the printer using system tools or terminal commands depending on your distribution.
Updating PCL Drivers for Better Performance
Driver updates fix bugs, improve performance, and sometimes add new features. To update:
- Check the manufacturer’s website regularly for new driver versions.
- Uninstall the old driver if necessary before installing the latest one.
- On Windows, you can also use Device Manager → Update Driver for automatic updates.
Troubleshooting Common PCL Driver Issues

Even with the right PCL Driver installed, printing problems can still occur due to software conflicts, network errors, or outdated drivers. Here are the most common issues and practical solutions to get your printer running smoothly again.
Printer Not Recognized
One frequent problem is when the printer doesn’t appear on your computer, even after installing the driver. This can happen due to connectivity issues or incorrect driver selection.
Solutions:
- Check the USB or network cable connection if using a wired printer.
- For wireless printers, confirm that both devices are on the same Wi-Fi network.
- Ensure the correct PCL Driver version is installed for your printer model and operating system.
Print Jobs Stuck in Queue
Sometimes documents get stuck in the print queue, preventing new jobs from being processed. This is often related to spooler service errors.
Solutions:
- On Windows, open Services and restart the Print Spooler service.
- Cancel all pending jobs in the printer queue before resending the document.
- Check for any paper jams or printer-side errors.
Incorrect Page Formatting or Missing Graphics
If your printouts show text misalignment or missing graphics, it may indicate driver compatibility issues or corrupted print files.
Solutions:
- Reinstall or update the PCL Driver to the latest version.
- Try switching between PCL5 and PCL6 drivers to see which works better for your needs.
- For complex graphics, ensure your application is exporting files correctly before printing.
Slow Printing Speed
While PCL is generally faster than many other drivers, network congestion or outdated software can slow down print jobs.
Solutions:
- Use a wired connection for large print jobs to reduce delays.
- Update printer firmware and drivers to improve performance.
- Avoid using “High Quality” settings unless necessary, as they can slow down printing.
Frequent Driver Crashes
Occasionally, drivers may become unstable after system updates or printer firmware changes.
Solutions:
- Completely uninstall the driver before reinstalling the latest version.
- Roll back recent Windows Updates if the problem started after a system patch.
- Check the printer manufacturer’s support page for hotfixes or compatibility notes.
PCL Drivers vs Other Print Drivers
Choosing the right printer driver can be confusing with so many options available, including PCL, Universal Printer Drivers, PostScript, Host-Based Drivers, GDI, and XPS. Each driver type comes with unique strengths and limitations that affect speed, quality, and compatibility. Below is a detailed comparison to help you make the right choice.
vs Universal Printer Drivers
Universal Printer Drivers (UPDs) are designed to support multiple printer models from the same manufacturer. Their main advantage lies in simplified management since you only need one driver for many devices. However, UPDs sometimes lack advanced printer-specific features that dedicated drivers like PCL provide.
- Pros: One driver for multiple printers, easy installation.
- Cons: May not support all advanced printer-specific functions.
vs PostScript Drivers
PostScript (PS) Drivers are widely used in graphic design and professional printing environments. They deliver outstanding output quality for complex graphics but often print slower than PCL, especially for text-heavy documents.
- Pros: Superior graphic quality, ideal for publishing and design.
- Cons: Slower printing speed, requires more printer memory.
vs Host-Based Drivers
Host-Based Drivers (sometimes called Windows-Only Drivers) rely on the computer to process all print data before sending it to the printer. They are easy to install but lack flexibility for multi-platform environments and are usually slower than PCL Drivers for large print jobs.
- Pros: Simple installation, good for home users.
- Cons: Performance depends on the computer, not suitable for heavy office printing.
vs GDI
GDI (Graphics Device Interface) Drivers work closely with Windows to render print data on the computer instead of the printer. They are lightweight but only compatible with Windows systems and lack advanced printing features.
- Pros: Lightweight, simple setup for Windows.
- Cons: Windows-only compatibility, limited print quality options.
vs XPS
XPS Drivers were developed by Microsoft using the XML Paper Specification. They offer good print quality for modern Windows systems but have limited support for older printers and non-Windows platforms.
- Pros: Good quality in modern Windows environments, supports XPS document format.
- Cons: Limited compatibility outside Windows ecosystems.
Comprehensive Comparison Table: PCL vs Other Printer Drivers
| Driver Type | Speed & Efficiency | Print Quality | Platform Compatibility | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCL Driver | Fast & efficient | High for text & basic graphics | Multi-platform | Office documents, everyday printing |
| Universal Printer Driver | Moderate | Depends on printer model | Multi-platform | Large-scale printer management |
| PostScript Driver | Slower for text printing | Superior for complex graphics | Multi-platform | Graphic design, professional publishing |
| Host-Based Driver | Depends on PC performance | Standard quality | Windows only | Home users, light document printing |
| GDI Driver | Moderate | Limited for high-res printing | Windows only | Basic Windows printing tasks |
| XPS Driver | Moderate | Good in Windows environments | Windows modern systems only | XPS document printing in Windows ecosystems |
Best Practices for PCL Driver Maintenance

Proper maintenance of PCL Drivers ensures consistent print quality, minimizes downtime, and extends the lifespan of your printer. Whether you’re using PCL5, PCL6, or Universal PCL Drivers, following these best practices will help keep your printing environment stable and efficient.
1. Keep Drivers Updated Regularly
Printer manufacturers frequently release driver updates to fix bugs, improve compatibility, and enhance performance.
- Check the official website for the latest PCL Driver versions at least once every few months.
- Avoid third-party sites to reduce the risk of malware or outdated drivers.
- Use tools like Windows Update or manufacturer utilities for automatic driver updates when available.
2. Use the Correct PCL Driver Version
Not all printers support the same PCL version. For example:
- PCL5 works well for basic text printing and legacy systems.
- PCL6 provides better resolution, speed, and graphics capabilities.
- Universal PCL Drivers simplify printer management across multiple models.
Always check your printer manual or manufacturer’s website to confirm driver compatibility.
3. Remove Old or Unused Drivers
Keeping outdated drivers installed can cause conflicts or printing errors.
- On Windows, use Print Management or Device Manager to remove unused drivers.
- Mac and Linux users can uninstall drivers through system settings or terminal commands.
This helps prevent accidental selection of the wrong driver during printing.
4. Monitor Printer Performance
If you notice slower print speeds, formatting errors, or frequent connection issues, the driver might be outdated or corrupted.
- Reinstall the driver if problems persist after an update.
- Check printer firmware updates as well, since drivers and firmware work hand in hand for optimal performance.
5. Backup Working Driver Configurations
For office environments, it’s a good idea to back up a stable driver configuration.
- Keep a copy of the driver installation files and settings.
- This saves time when restoring or installing on multiple computers.
Conclusion
The PCL Driver remains one of the most reliable and versatile printing drivers available today. From its speed and compatibility to the balance of quality and performance, PCL Drivers are a top choice for businesses and home users alike. By learning how to install, update, and maintain them properly, you can avoid common printing issues and ensure smooth operations across multiple devices and platforms.
Whether you compare it with PostScript, Host-Based, or Universal Drivers, PCL stands out for its efficiency and ease of use — making it an essential component in modern printing workflows.
FAQs About PCL Drivers
What is the main difference between PCL5 and PCL6 Drivers?
PCL6 offers better print quality, faster processing, and improved graphics handling compared to PCL5, which is better suited for simple text documents and legacy systems.
Can I use PCL Drivers on both Windows and macOS?
Yes, most PCL Drivers support multiple platforms including Windows, macOS, and some Linux distributions, depending on the printer model and manufacturer support.
How often should I update my PCL Driver?
Check for updates at least every few months or whenever you experience performance issues. Manufacturers often release updates to fix bugs and enhance compatibility.
Why is my printer not printing even after installing the PCL Driver?
Common causes include wrong driver version, connectivity issues, or print queue errors. Verify the correct driver version and restart the printer spooler service if needed.
Are Universal PCL Drivers as good as dedicated PCL Drivers?
Universal PCL Drivers simplify management across multiple printer models but may lack certain advanced features available in dedicated model-specific PCL Drivers.